2023-06-25T18:18:40
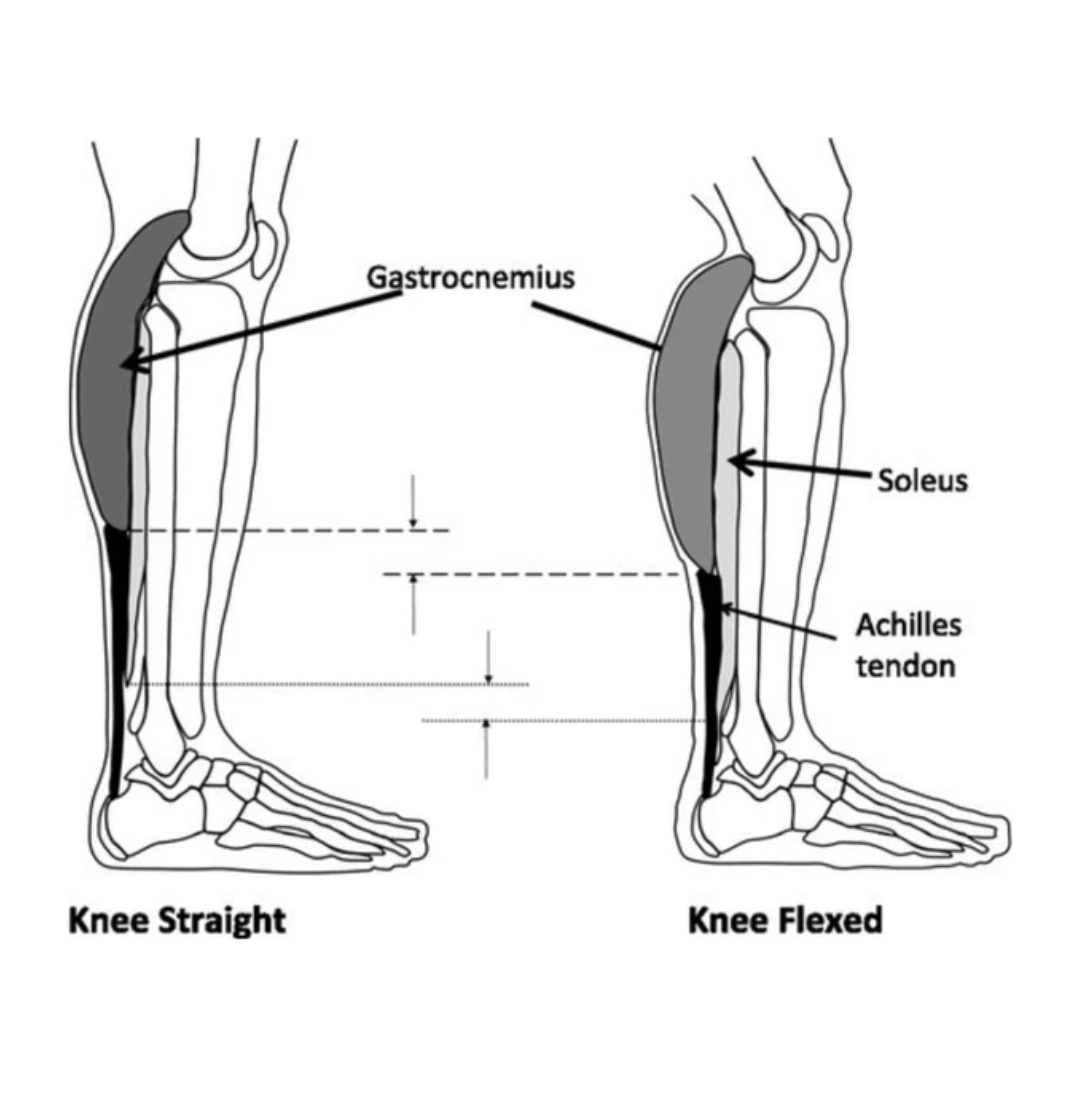
Physiotherapy clinic in Tambaram Are you Looking for Physiotherapy Treatment in Tambaram, Sunshine Super Speciality Physiotherapy Clinic, We Provide Electrotherapy, Exercise and Manual Therapy, Orthopedic, Neuro, Cardio, Pediatric, Sports and Geriatric Rehabilitation, Post Operative Physiotherapy Treatment, Fracture Rehabilitation, pain free movement. Trigger Point Therapy | Treating Soleus | Injury Assessment | Self Help Tips Gastrocnemius soleus trigger point release From a dynamic postural viewpoint, the soleus prevents the body falling forward at the ankle joint during standing In gait, the muscle eccentrically decelerates subtalar joint pronation and internal rotation of the lower leg at heel-strike. It also decelerates dorsi flexion of the foot. Spasm or myofascial trigger points in the soleus can be the origin of achilles pain, tight hamstrings, lower back pain, night cramp, and even headaches. The soleus typically refers pain into the posterior aspect and plantar surface of the heel and to the distal end of the Achilles tendon. A rare myofascial trigger point spreads pain to the ipsilateral sacroiliac joint, and can also refer pain to the jaw in extreme cases. Anatomy Part of the triceps surae. The soleus is so called because its shape resembles a fish. The calcaneal tendon of the soleus and gastrocnemius is the thickest and strongest tendon in the body. Origin Posterior surfaces of head of bula and upper third of body of bula. Soleal line and middle third of medial border oftibia. Tendinous arch between tibia and bula. Insertion With tendon of gastrocnemius into posterior surface of calcaneus. Soleus Trigger Points Soleus - Common Trigger Point Sites Action Plantar flexes ankle joint. Frequently in contraction during standing, to prevent body falling forward at ankle joint, i.e. to offset line of pull through body’s center of gravity, thus helping to maintain upright posture. Antagonist: tibialis anterior. Nerve Tibial nerve, L5, S1, 2. BASIC FUNCTIONAL Movement Example: standing on tiptoes. Trigger point referred pain patterns Pain in distal Achilles tendon and heel to posterior half of foot. Calf pain from knee to just above Achilles tendon origin. 4–5 cm zone of pain in ipsilateral sacroiliac region (rare). Indications Calf/heel/posterior knee pain, chronic/long-term use of high-heeled shoes, planter fasciitis, chronic calf shortening, calf pain walking stairs, low back pain, leg cramps. Causes Post-fracture splinting, poor orthotics, prolonged driving, sports (e.g. running, soccer, cycling, climbing, skiing, rowing machine), footwear (high heels), PSLE, occupational standing, direct blow/ trauma, pressure on calf. Differential Diagnosis Achilles tendonitis. Compartment syndrome. Vascular disease. Heel spur. Fasciitis. Subtalar joint problems. Venous pump mechanisms. Tendon rupture. Baker’s cyst. Shin splints. Stress fracture. Leg length discrepancy. Connections Popliteus, gastrocnemius, tibialis posterior, quadratus plantae (of foot), abductor hallucis (of foot), piriformis, occasionally to jaw. Self Help Self-massage techniques can be helpful; you can even use the opposite knee. Balls and pressure tools may be used but not by the novice, as the muscle is deep and there are many superficial and deep veins in the area. Stretching is excellent for disabling trigger points in the calf muscles. Use of foam rollers can be effective. General Advice Change footwear. Change and vary running techniques/running surface. Change/avoid high-heeled shoes. Regular stretching. Leg rests at home and at work. Use of cold. Massage after sports, with warm up before and cool down after. Posture. SUNSHINE ® SUPER SPECIALITY PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC - #DrParthiban #Sunshinephysioclinic.in #Physiotherapyclinicintambaram DR.M.P. PARTHIBAN.M.P.T (Ortho), Chief Orthopedic Physiotherapist, Call for Appointments: - 9345122177 East Tambaram, CHENNAI