2024-10-18T17:46:52
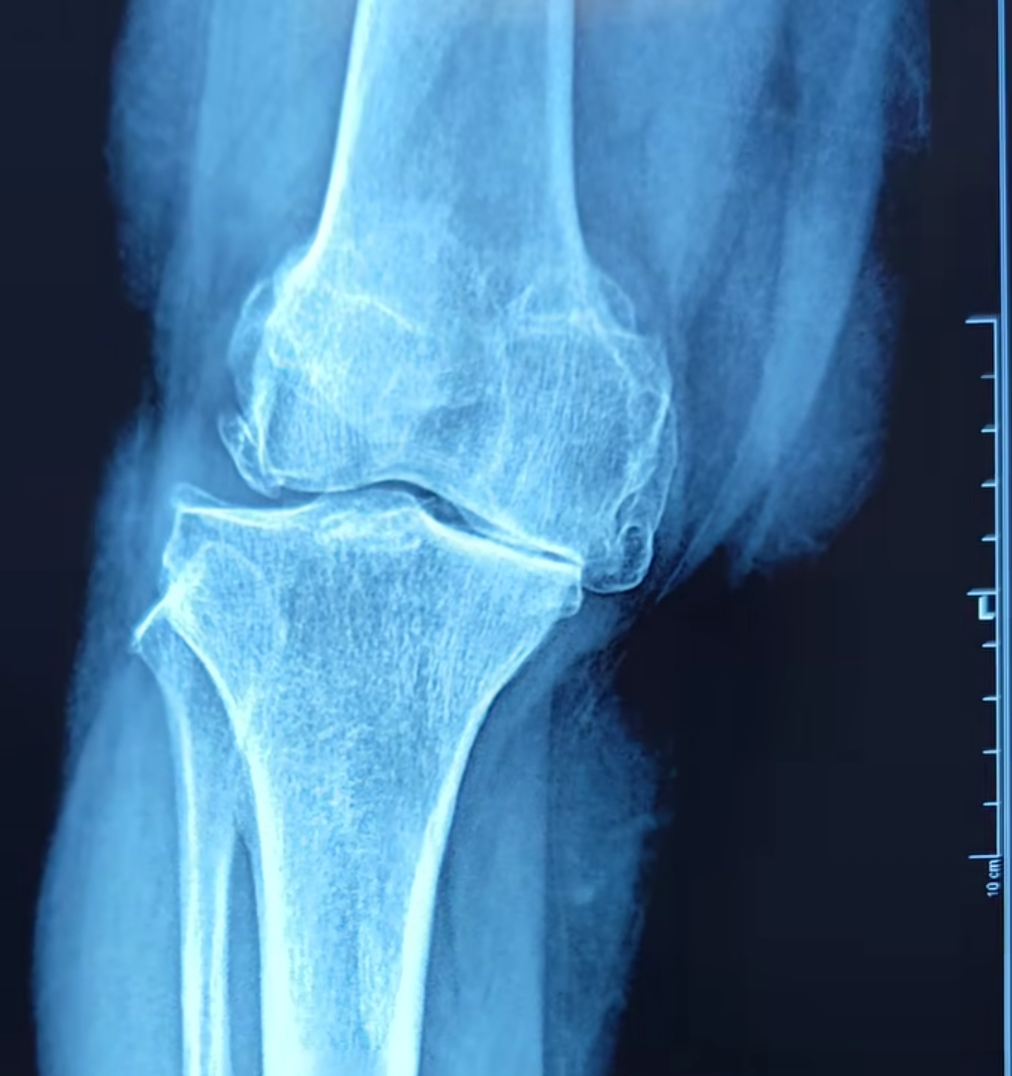
Physiotherapy clinic in Tambaram Are you Looking for Physiotherapy Treatment in Tambaram, Sunshine Super Speciality Physiotherapy Clinic, We Provide Electrotherapy, Exercise and Manual Therapy, Orthopedic, Neuro, Cardio, Pediatric, Sports and Geriatric Rehabilitation, Post Operative Physiotherapy Treatment, Fracture Rehabilitation, pain free movement. Knee Osteoarthritis Pathophysiology of Knee Osteoarthritis Knee osteoarthritis is a complex condition involving the entire joint, including the cartilage, subchondral bone, synovium, and surrounding ligaments and muscles. 1. Cartilage Degeneration: • Cartilage is the smooth, rubbery tissue that covers the ends of bones in the joints, allowing for smooth movement. • In OA, cartilage breaks down and wears away, causing the bones to rub against each other. This leads to pain, swelling, and loss of joint motion. 2. Bone Changes: • As cartilage erodes, the underlying bone becomes exposed and begins to thicken, forming osteophytes (bone spurs). • The bone beneath the cartilage (subchondral bone) may harden and develop cysts or microfractures, further contributing to joint pain and deformity. 3. Synovial Inflammation: • The synovium, which lines the joint, can become inflamed and thickened, producing excess synovial fluid, leading to joint swelling (effusion)synovial fluid, leading to joint swelling (effusion). 4. Ligament and Muscle Involvement: • The weakening of muscles around the knee and the stretching of ligaments can lead to joint instability, exacerbating the pain and reducing function. Detailed Symptoms The symptoms of knee OA vary in severity and can progress over time: 1. Pain: • Pain typically worsens with activity andimproves with rest. • It may initially occur during or after movement but can progress to persistent pain, even at rest or during the night. 2. Stiffness: • Morning stiffness is common but usually lasts less than 30 minutes. • Stiffness may also occur after prolonged sitting or inactivity. 3. Swelling: • Joint effusion (swelling) is due to the excess synovial fluid in the joint. • The knee may feel warm and appear swollen. 4. Reduced Range of Motion: Difficulty in fully bending or straightening the knee. • Over time, muscle atrophy and joint contractures can further limit motion. 5. Deformity: • In advanced stages, the joint may become deformed, leading to a bow-legged (varus) or knock-kneed (valgus) appearance. #physicaltherapy #painrelief #physiotherapy #osteoarthritis #injuryprevention #knee #kneepain SUNSHINE ® SUPER SPECIALITY PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC - #DrParthiban #Sunshinephysioclinic.in #Physiotherapyclinicintambaram #Physiotherapyclinicnearme DR.M.P. PARTHIBAN.M.P.T (Ortho), Chief Orthopedic Physiotherapist, Call for Appointments: - 9345122177 East Tambaram, CHENNAI